Advanced Continuous Casting Machines | Turnkey Solutions | Global Supplier
Produce high-quality steel billets, blooms, and slabs with precision, efficiency, and uniform quality. We are a professional manufacturer and global supplier of continuous casting machines, with over 15 years of experience in designing, producing, and exporting steel casting equipment. Our complete CCM lines delivering high-quality steel billets, blooms, and slabs for construction, machinery, automotive, and industrial applications.
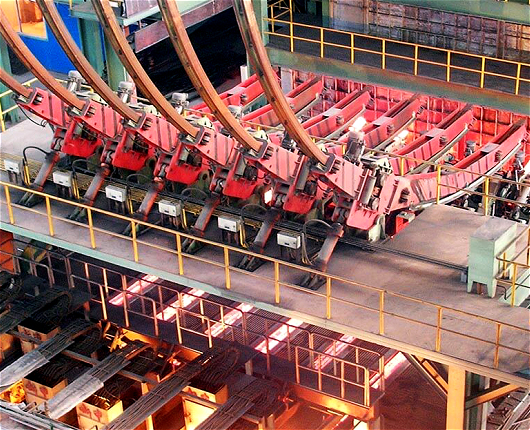
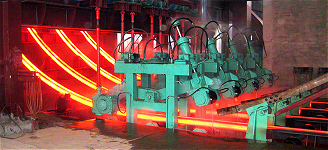


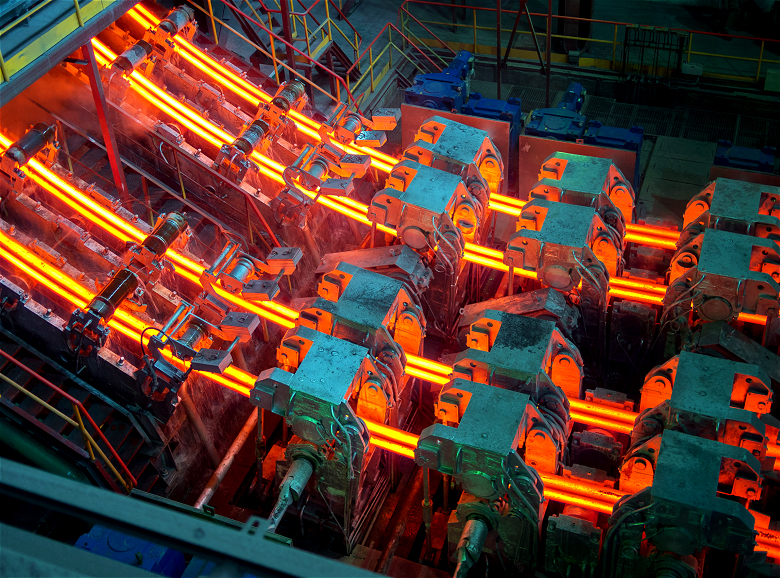
In the links of liquid level control, online width adjustment, non-sinusoidal vibration, secondary cooling water control, online light pressure, etc., all digital control is realized, which improves the accuracy and stability of equipment operation.
Customized design according to the actual needs of customers.
The billet shell is cooled evenly and is not affected by the bending and straightening. The cooling, solidification and drawing process of the molten steel can be completed in a relatively short time, which greatly improves the production efficiency.
The cooling and drawing speed can be controlled during the solidification of the molten steel to achieve better product quality. At the same time, online detection, control and adjustment can be carried out to reduce the defective rate and improve the reliability and durability of the product.




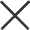
The molten metal is poured from the furnace into the casting pool of the continuous casting machine. Then, the molten metal is injected into the mold through the gate in the casting pool. In the mold, the molten metal will gradually cool and solidify to form a continuous billet. During the cooling and solidification process, a water cooler is needed to control the temperature of the billet to ensure that the billet is cooled evenly and stably. At the same time, a pulling mechanism is needed to pull the billet so that it can be smoothly separated from the mold to form a complete continuous billet. After the billet is cooled and solidified, it is necessary to remove the scale and molten iron residue on the surface of the billet. Next, the billet will be cut by a cutting machine to form a casting billet that meets the requirements.

| Type |
Billet size |
Productivity |
Flow |
Cutting way |
| R2.25 | 60*60 | 3T/hour | 1 | Flame cutting |
| R3 | 60*80 | 8T/hour | 1 | Flame cutting |
| R3.5 | 80*80 | 10T/hour | 2-3 | Flame cutting |
| R4 | 90*90 | 20T/hour | multi-flows | Hydraulic |
| R5.25 | 100*100 | 30T/hour | multi-flows | Hydraulic |
*The output will vary according to different materials, feed particle size and other factors
Save Time! Get A Detailed Quotation Quickly.