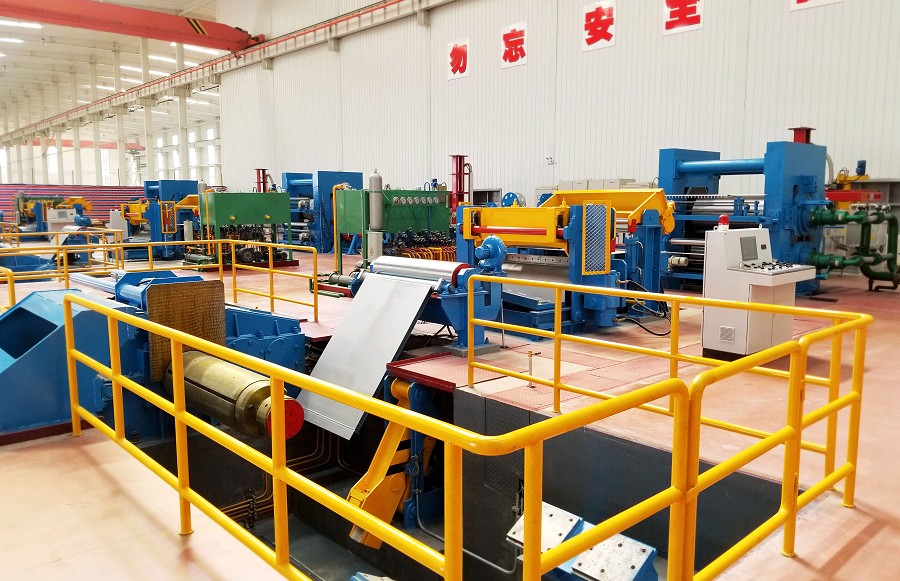
The rolling mill adopts the U-shaped double-column frame, but the frame does not bear the rolling force in the vertical direction, it only needs to bear the horizontal impulse when the rolling stock bites in and out and the horizontal component during rolling. Therefore, it can be designed into the light section structure, and the frame is positioned by the side of the bearing seat, which has a large bearing area and improves the stability of the rolling mill during rolling.
The section of the column is L-shaped, which ensures sufficient strength and rigidity, and facilitates the installation of the lateral adjustment device and the guiding device. The lateral alignment device is close to the centerline of the roll, which is advantageous for increasing the axial working stability of the roll. There is still a wedge-shaped lifting and adjusting device at the lower part of the frame. Both sides can be single-acting or interlocking. When changing the roller, it is used to adjust the level of the roll and the height of the rolling line to adapt to the change of the roll diameter of the spare roll or the height error of the bearing seat. Basically, no adjustment is made during rolling. The guides are attached to the bosses with T-slots on the front and rear sides of the frame. Generally, no adjustment is required during rolling and roll changing, and stable operation can basically be achieved.
Most of the roller bearings used in the old rolling mills are bakelite tiles. The deformation caused by compression during rolling is large, and the deformation of the bakelite tiles and the fit between the inner and outer sides are not regular, and it is difficult to control, resulting in the manual adjustments for old-fashioned rolling mills are frequent and the precision of the rolled material is low. This rolling mill adopts four rows of short cylindrical rolling bearings with large bearing capacity, which improves the bearing rigidity and running precision of the rolling mill, and is convenient for assembly and disassembly.
The HGR rolling mill also adopts double-half outer ring radial thrust ball bearings to withstand the axial load in rolling or transmission. The axial clearance can be controlled by grinding in the range of 0.10 – 0.20mm during the assembly and the two ends of the roll are locked by the positive and negative thread locking device to ensure that the axial yaw control of the roller is within the allowable value range, so as to improve the product quality.